Why do omega-6:3 fatty acids balance matter?
The delicate balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in our diets plays a pivotal role in our overall health. These essential fats are not just sources of energy but also integral to the structure and function of our cells.
When the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio aligns with the recommended 4:1 ratio, our cells flourish, maintaining their integrity, fluidity, and efficiency in nutrient absorption and waste elimination. This balance also helps keep our inflammatory responses in check, preventing them from becoming overly reactive.
Unfortunately, today's reality paints a different picture, with global averages skewing closer to 15:1, leading to chronic low-level inflammation and far-reaching consequences.
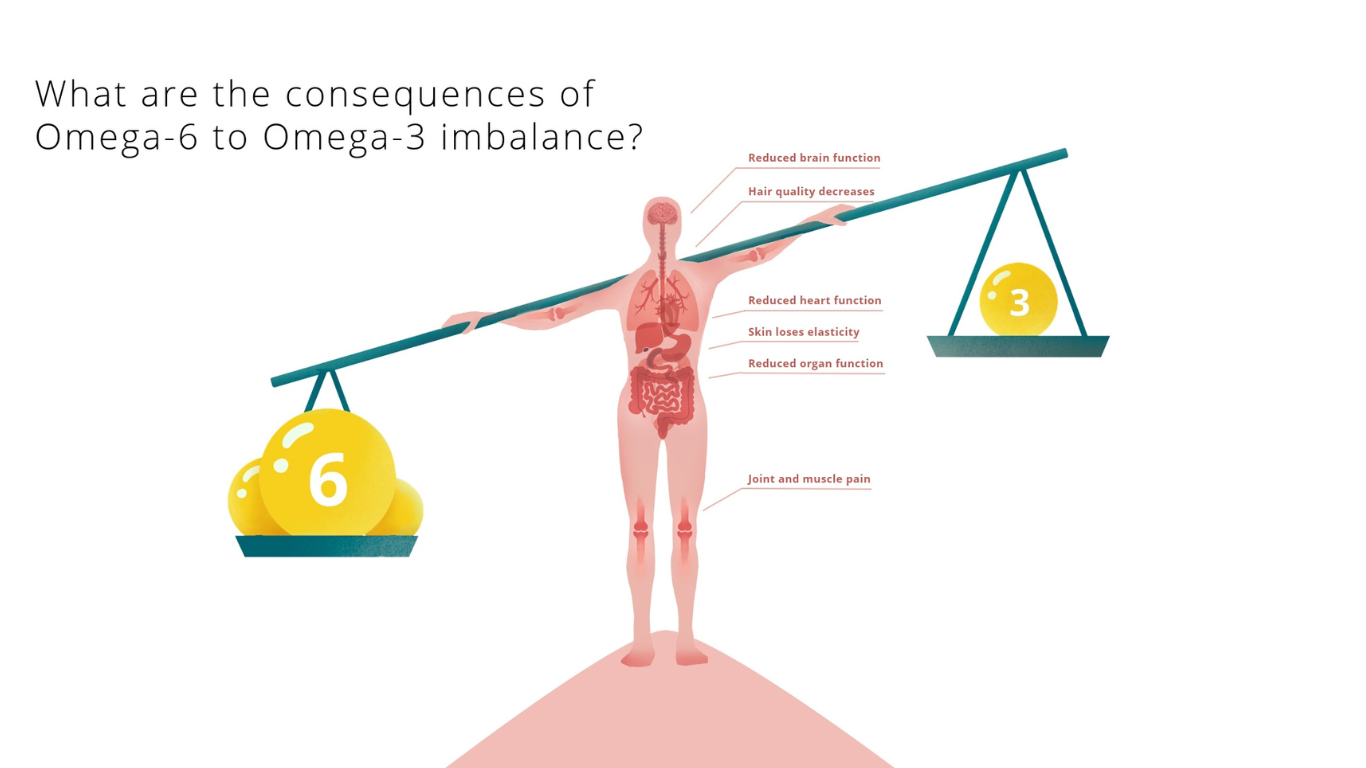
The Omega-6 to Omega-3 Imbalance
Modern Western diets are rich in omega-6 fatty acids and often lack omega-3 fatty acids, creating a significant imbalance compared to our evolutionary diet. Excessive omega-6 intake, coupled with a high omega-6:3 ratio, contributes to the development of various diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. On the other hand, increased omega-3 levels (a lower omega-6:3 ratio) exhibit protective effects.
The ideal ratio may vary based on the disease under consideration, as chronic diseases have multifactorial causes. Therefore, the therapeutic dose of omega-3 fatty acids may depend on the severity of the disease and individual genetic predisposition.
Achieving a lower omega-6:3 fatty acid ratio is desirable to reduce the risk of prevalent chronic diseases, both in Western societies and developing countries.
The Omega-3 Index
The Omega-3 Index, established by Harris and Von Schacky in 2004, serves as a measure of red blood cell membrane EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) composition, indicating the proportionality of total fatty acids. Maintaining a healthy Omega-3 Index is vital for overall well-being.
Negative Health Consequences of Omega-3 Deficiency
Insufficient omega-3 intake can result in various health issues, including:
• Impaired cognitive function: Omega-3 deficiency may lead to memory and cognitive impairments.
•Defective child development: Omega-3 is crucial for the neurological development of children.
•Gut dysfunction: A lack of omega-3 can negatively affect gut health.
•Increased risk of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD): Omega-3 helps reduce the risk of heart disease.
•Increased risk of certain cancers: Omega-3 intake can lower the risk of specific types of cancer.
•Skin disorders: Omega-3 contributes to healthy skin and hair.
•Sleep disorders: Omega-3 may help improve sleep quality.
Benefits of Adequate Omega-3 Levels
Having sufficient omega-3, both in terms of ratio and index, offers numerous health advantages, such as:
•Lowered risk of CVD: Omega-3 helps reduce the risk of heart disease.
•Reduced pain and symptoms of arthritis: Omega-3 has anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate arthritis-related discomfort.
•Improved cognitive function: Omega-3 supports brain health and mental abilities.
•Enhanced memory: Adequate omega-3 levels are associated with improved memory.
•Improved gut health: Omega-3 helps maintain a healthy gut.
•Better skin and hair condition: Omega-3 promotes skin and hair health.
•Decreased circulating LDL cholesterol: Omega-3 may help lower "bad" cholesterol levels.
The Global Omega-3 Crisis
Over the past five decades, there has been a noticeable and concerning reduction in the consumption of fatty fish, such as salmon, bluefin tuna, mackerel, anchovies, and sardines, in modern industrial nations. This decline in fatty fish intake has now extended to the Mediterranean countries, marking a global shift in dietary patterns.
Unfortunately, this shift is accompanied by a growing global health crisis linked to omega-3 deficiency, which is exacerbated by the increasing consumption of omega-6 fatty acids due to the industrialization of food and the widespread availability of ultra-processed foods (UPFs).
The importance of the omega-6:3 ratio and the Omega-3 Index cannot be overstated when it comes to maintaining good health and preventing chronic pain and diseases. Omega-3 deficiency has been a well-documented concern for decades, and the consequences are now becoming increasingly evident in the global population's health.
The outcome is a dietary-induced imbalance of cellular health. As cells are the very thing we are made of, and as every cell is a replica of the cell from which it originated, there is a cascade of adverse health consequences when a deficiency functions at such a fundamental level. The worst part is that this disaster has been visible on our horizon for a long time.
Individuals must be aware of the significance of these ratios and take action to balance their intake of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. By adopting a diet rich in omega-3 sources, such as fatty fish and supplements, and reducing the consumption of omega-6-heavy processed foods, we can better safeguard our cellular health, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote overall well-being.
The key to unlocking the full potential of protein synthesis and, by extension, achieving optimal health lies in preserving the omega 6:3 ratio and Omega-3 Index. It's time to prioritize these essential fatty acids for a healthier future.
When I received my omega 6:3 balance blood test result, I was shocked because I was out of balance. My ratio was 16:1! At that time, I had chronic shoulder pain ( bad inflammation ).
I eat healthy and almost never eat processed food or fried food. My husband and I cook from scratch and almost never eat out. I don’t really eat fish, but I took omega-3 supplements. I found out that most omega-3 supplements don’t work, but I found one that did, and some things we were eating, for example, some sauce, had some additives that can be toxic.
In my next blog post, I will tell you how I fixed my omega 6:3 balance and recovered from chronic shoulder pain.
Chronic Pain and Inflammation